The Struggle for Silesia and Continental Dominance

The Geopolitical Background
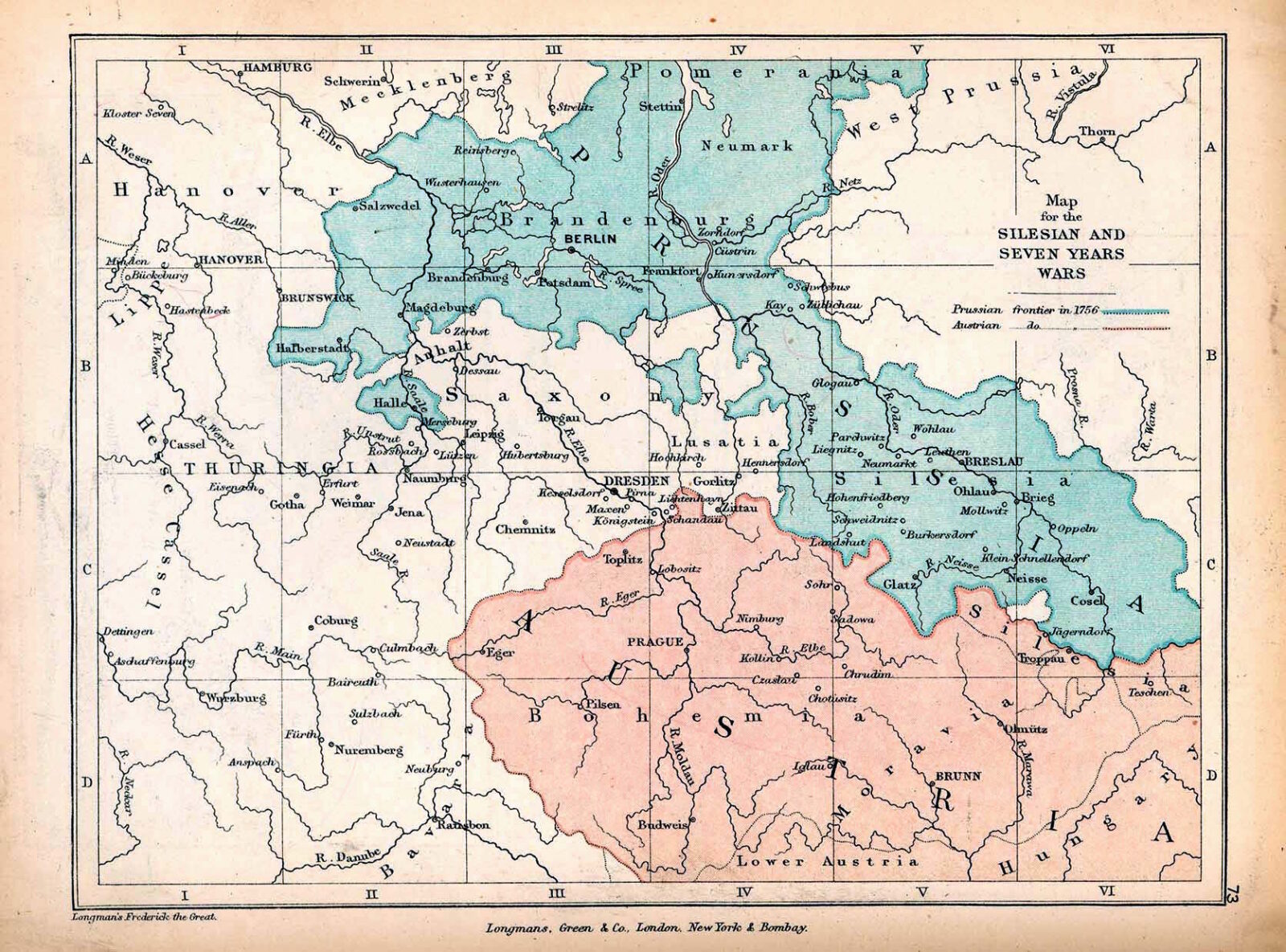
The war's roots lay in the complex web of European alliances and rivalries, and it was a continuation of hostilities initiated in the earlier Silesian Wars. The struggle for supremacy between major powers such as Britain, France, Austria, and Prussia set the stage for a conflict that extended far beyond European borders. The immediate cause was the territorial disputes involving Silesia, a region rich in resources and strategically located, which Prussia had seized from Austria in the War of the Austrian Succession.

Origins and Outbreak
The War of the Austrian Succession had concluded with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, but unresolved issues and grudges persisted. Austria, under Maria Theresa, was intent on regaining Silesia and Prussia, led by Frederick the Great, acted preemptively against its enemies. Starting with the invasion of Saxony in 1756, this move triggered a series of military operations across Silesia, Bohemia, and Upper Saxony.
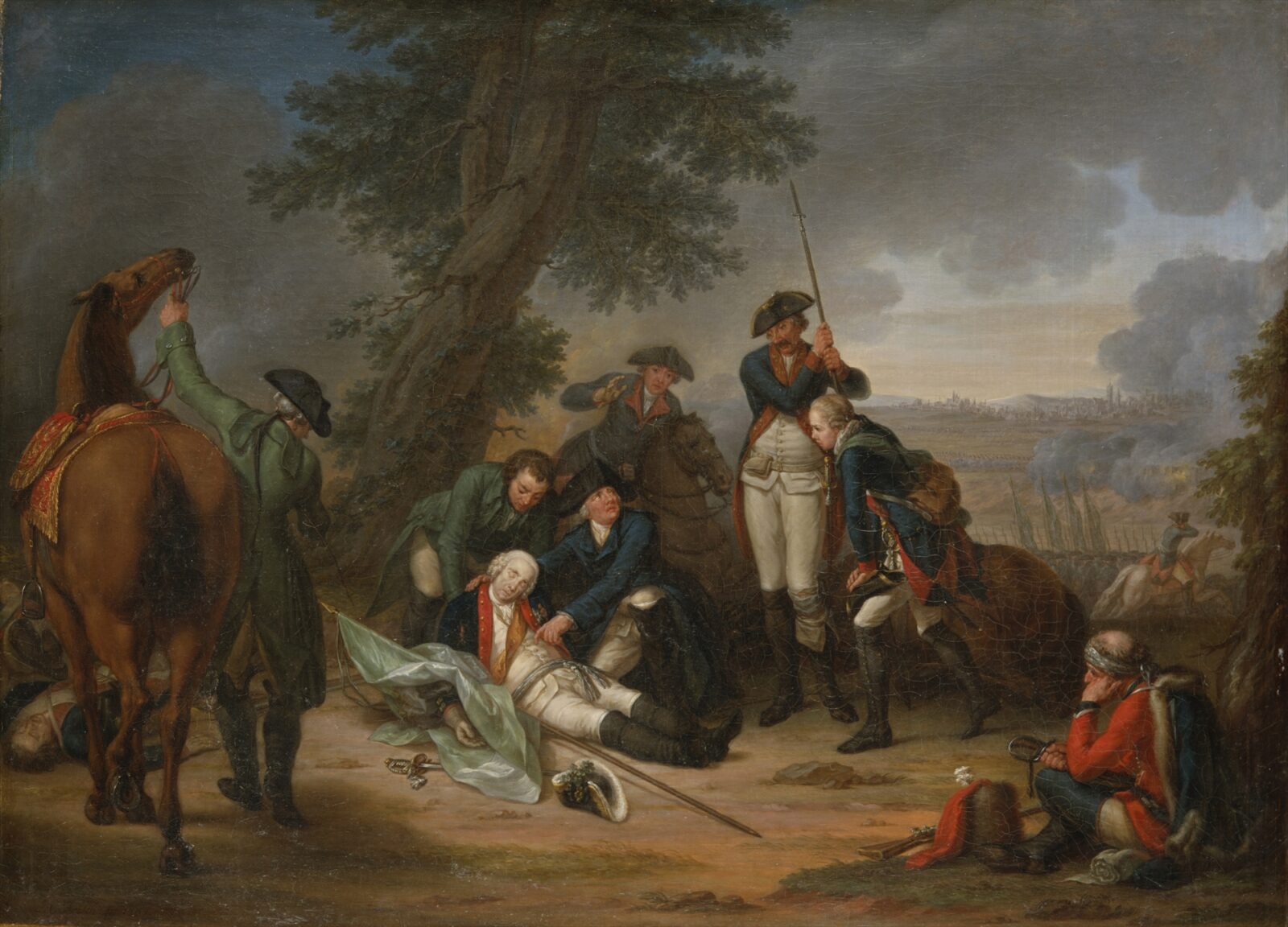
The initial phases of the war saw rapid Prussian advances, but the tide turned with the entry of new belligerents on the Austrian side. The war featured notable battles like Lobositz, Prague, and Kolín, highlighting Frederick's military prowess but also the limits of Prussian capabilities against a coalition of adversaries.

Major Battles and Strategies
The Seven Years' War witnessed several significant battles that demonstrated the military strategies of the 18th century. Key battles included the Battle of Plassey in India, which marked the beginning of British dominance in the subcontinent, and the Battle of Quebec in North America, a turning point in the colonial struggle between Britain and France. In Europe, the Battle of Rossbach and the Battle of Leuthen were notable for Frederick the Great's military tactics, which enabled Prussian victories against numerically superior forces.

The Global Dimensions of the Conflict
The Seven Years' War extended beyond European borders, affecting colonial empires in Asia and North America. In India, the Battle of Plassey marked the beginning of British dominance, while in North America, the French and Indian War saw critical engagements like the Battle of Quebec. This global dimension underlines the war's significance as a precursor to later worldwide conflicts and as a catalyst for the rise of the British Empire.

Stalemate and Treaty of Hubertusburg
By the war's end, exhaustion and depleted resources led to a stalemate. The Treaty of Hubertusburg in 1763 restored the status quo ante bellum in terms of territorial changes but marked a diplomatic victory for Prussia, confirming its control over Silesia. The war significantly altered the European power balance, establishing Prussia as a major power and setting the stage for future conflicts in the region.

Your Connection To The Seven Years' War
Lower Silesia, with its strategic location and economic importance, was one of the central theaters of this war. The region around The Lodge witnessed several military campaigns, troop movements and battles.
Duration:
1756 - 1763
Soliders:
> 1 mio
Losses:
> 1 mio